Elixir/Phoenix Security: What is CSRF via Action Reuse?
Michael Lubas, 2023-03-28

The typical description of cross site request forgery (CSRF) involves a POST request being triggered without a secure token. If there’s a state changing HTML form making a POST, with a CSRF token, that’s validated by the server, that should be secure. Consider a web application where both a GET and POST request can perform the same state changing action. This is likely not the developer’s intention, but that is the root of most security problems in software.
Is CSRF possible with a GET request? Yes, in fact it’s worse than a POST request, because GET requests should never be used to perform state changing actions in a web application (place an order, transfer money, etc). The Sobelow finding Config.CSRFRoute: CSRF via Action Reuse states:
This type of CSRF is flagged by `sobelow` when state-changing
routes share an action with GET-based routes. For example:
get "/users", UserController, :new
post "/users", UserController, :new
In this instance, it may be possible to trigger the POST
functionality with a GET request and query parameters.A Google search for “Action Reuse CSRF” does not return any useful links, and the above text may be confusing if you are thinking of CSRF in terms of POST requests and CSRF tokens. Why does the router pattern above, the:
get "/users", UserController, :new
post "/users", UserController, :newresult in CSRF? Isn’t CSRF related to HTML forms and HTTP requests? Let’s use Potion Shop to explain.
@ potion_shop % mix sobelow
...
-----------------------------------------------
Config.CSRFRoute: CSRF via Action Reuse - High Confidence
File: lib/carafe_web/router.ex
Action: edit_bio
Line: 98
-----------------------------------------------The relevant lines in router.ex:
scope "/", CarafeWeb do
pipe_through [:browser, :require_authenticated_user]
get "/users/settings/edit_bio", UserSettingsController, :edit_bio
post "/users/settings/edit_bio", UserSettingsController, :edit_bioIn Potion Shop, you can update your bio from the settings page:
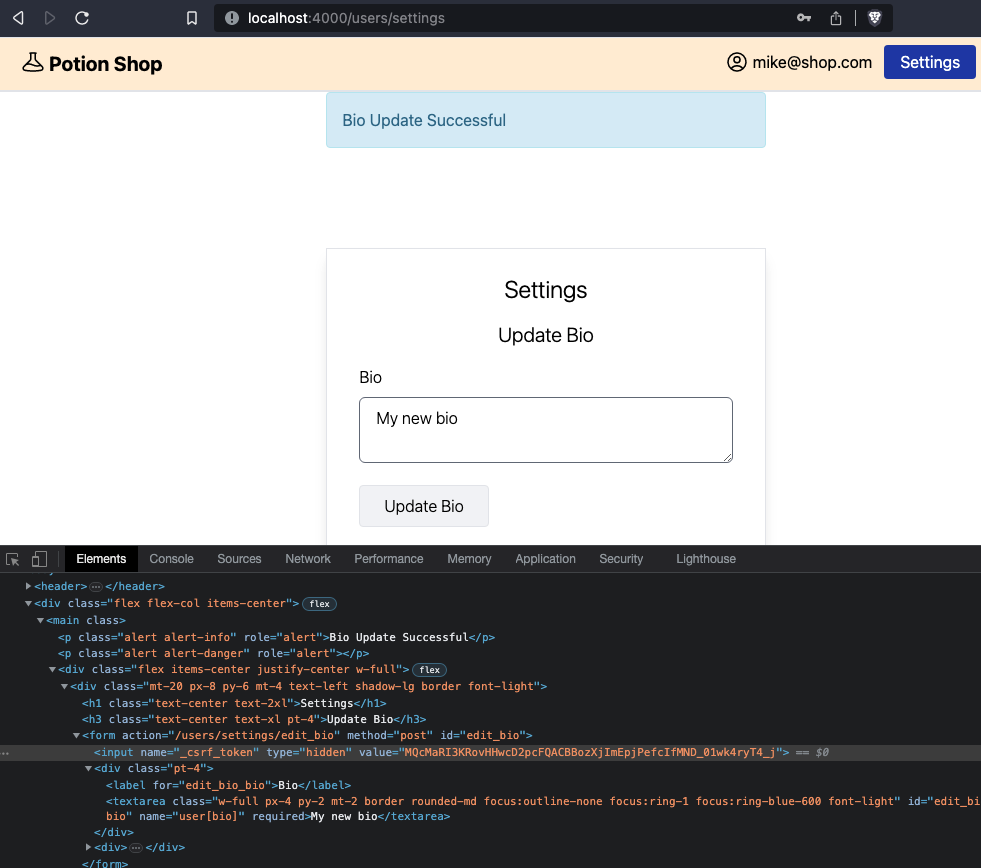
Notice that the form to edit the bio has an action to /users/settings/edit_bio, with a method of POST, and a valid CSRF token. In router.ex:
pipeline :browser do
plug :accepts, ["html"]
plug :fetch_session
plug :fetch_live_flash
plug :put_root_layout, {CarafeWeb.LayoutView, :root}
plug :protect_from_forgery
plug :put_secure_browser_headers
plug :fetch_current_user
end
The :browser pipeline has :protect_from_forgery enabled, so this form should not be vulnerable to CSRF. So why the Sobelow finding? The answer is that this form (making the POST request) is not vulnerable to CSRF, but the application is, via GET request.
What does a POST request look like to edit the user’s bio?
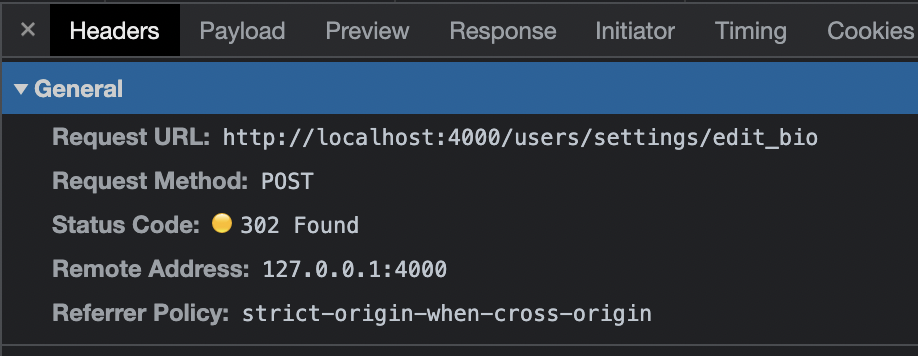
The body of the POST:
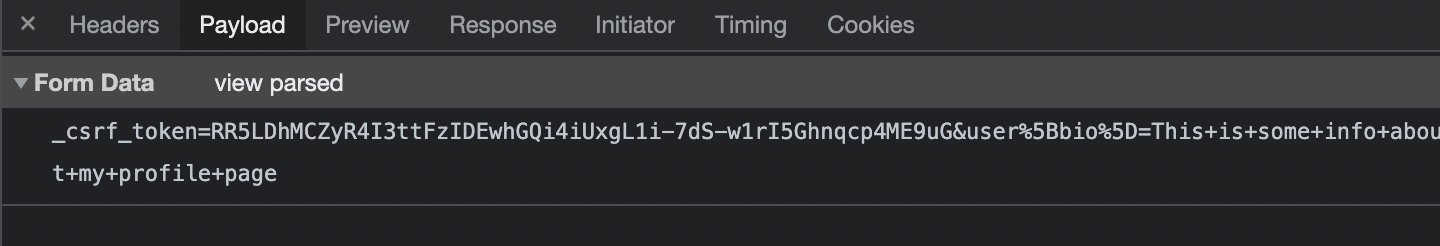
Notice the payload of the POST request:
_csrf_token=MQcMaRI3KRovHHwcD2pcFQACBBozXjImEpjPefcIfMND_01wk4ryT4_j&user%5Bbio%5D=This+is+some+info+about+my+profile+page
(broken up)
_csrf_token=(ignore for now)
&
user%5Bbio%5D=This+is+some+info+about+my+profile+page
In Phoenix, that POST request goes to the UserSettingsController, to the :edit_bio action function:
scope "/", CarafeWeb do
pipe_through [:browser, :require_authenticated_user]
get "/users/settings/edit_bio", UserSettingsController, :edit_bio
post "/users/settings/edit_bio", UserSettingsController, :edit_biodef edit_bio(conn, %{"user" => params}) do
case Accounts.update_user_bio(conn.assigns.current_user, params) do
{:ok, _bio} ->
conn
|> put_flash(:info, "Bio Update Successful")
|> redirect(to: Routes.user_settings_path(conn, :edit))
{:error, changeset} ->
render(conn, "edit.html", bio_changeset: changeset)
end
end
This is the root cause of the vulnerability, %{"user" => params} can be set by a GET request. If you log into Potion Shop and visit the URL:
http://localhost:4000/users/settings/edit_bio?user%5Bbio%5D=Hacked+LOL
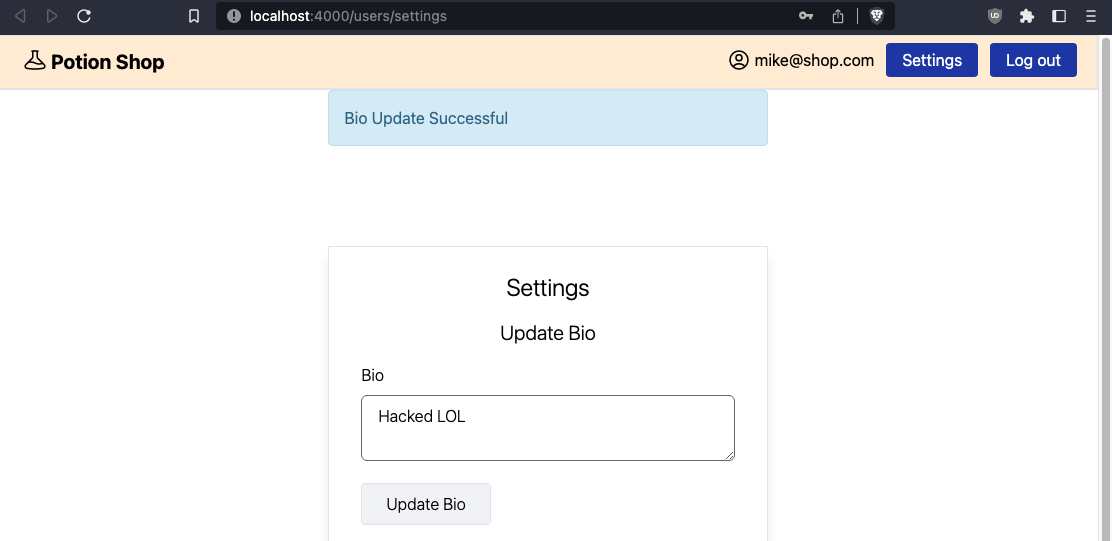
Your Bio is updated, without a POST request. This is because the GET request hits the same edit_bio/2 function in UserSettingsController as the POST request. The GET route is unnecessary, there’s no reason for it to exist. Deleting the line:
get "/users/settings/edit_bio", UserSettingsController, :edit_biofixes this vulnerability. Action reuse CSRF occurs when a misconfigured router introduces state changing GET requests in the application. Sobelow’s check for this vulnerability is very smart, and all Elixir/Phoenix developers should be aware of this issue.
Paraxial.io stops data breaches by helping developers ship secure applications. Get a demo or start for free.